Copyright 2022 Google LLC
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the “License”); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an “AS IS” BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
Adversarial training
The following code trains a convolutional neural network (CNN) to be robust with respect to the projected gradient descent (PGD) method.
The Projected Gradient Descent Method (PGD) is a simple yet effective method to generate adversarial images. At each iteration, it adds a small perturbation in the direction of the sign of the gradient with respect to the input followed by a projection onto the infinity ball. The gradient sign ensures this perturbation locally maximizes the objective, while the projection ensures this perturbation stays on the boundary of the infinity ball.
References
Goodfellow, Ian J., Jonathon Shlens, and Christian Szegedy. “Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples.”, https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572
Madry, Aleksander, et al. “Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks.”, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.06083.pdf
%%capture
%pip install jaxopt flax
import datetime
import collections
# activate TPUs if available
try:
import jax.tools.colab_tpu
jax.tools.colab_tpu.setup_tpu()
except KeyError:
print("TPU not found, continuing without it.")
from flax import linen as nn
import jax
from jax import numpy as jnp
from jaxopt import loss
from jaxopt import OptaxSolver
from jaxopt import tree_util
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 22})
import optax
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
Show on which platform JAX is running. The code below should take around 3 min to run on GPU but might take longer on CPUs.
print("JAX running on", jax.devices()[0].platform.upper())
JAX running on GPU
Flags = collections.namedtuple(
"Flags",
[
"l2reg", # amount of L2 regularization in the objective
"learning_rate", # learning rate for the Adam optimizer
"epochs", # number of passes over the dataset
"dataset", # one of "mnist", "kmnist", "emnist", "fashion_mnist", "cifar10", "cifar100"
"epsilon", # Adversarial perturbations lie within the infinity-ball of radius epsilon.
"train_batch_size", # Batch size at train time
"test_batch_size" # Batch size at test time
])
FLAGS = Flags(
l2reg=0.0001,
learning_rate=0.001,
epochs=10,
dataset="mnist",
epsilon=0.01,
train_batch_size=128,
test_batch_size=128)
def load_dataset(split, *, is_training, batch_size):
"""Load dataset using tensorflow_datasets."""
version = 3
ds, ds_info = tfds.load(
f"{FLAGS.dataset}:{version}.*.*",
as_supervised=True, # remove useless keys
split=split,
with_info=True)
ds = ds.cache().repeat()
if is_training:
ds = ds.shuffle(10 * batch_size, seed=0)
ds = ds.batch(batch_size)
return iter(tfds.as_numpy(ds)), ds_info
class CNN(nn.Module):
"""A simple CNN model."""
num_classes: int
@nn.compact
def __call__(self, x):
x = nn.Conv(features=32, kernel_size=(3, 3))(x)
x = nn.relu(x)
x = nn.avg_pool(x, window_shape=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2))
x = nn.Conv(features=64, kernel_size=(3, 3))(x)
x = nn.relu(x)
x = nn.avg_pool(x, window_shape=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2))
x = x.reshape((x.shape[0], -1)) # flatten
x = nn.Dense(features=256)(x)
x = nn.relu(x)
x = nn.Dense(features=self.num_classes)(x)
return x
# Hide any GPUs from TensorFlow. Otherwise TF might reserve memory and make
# it unavailable to JAX.
tf.config.experimental.set_visible_devices([], "GPU")
train_ds, ds_info = load_dataset("train", is_training=True,
batch_size=FLAGS.train_batch_size)
test_ds, _ = load_dataset("test", is_training=False,
batch_size=FLAGS.test_batch_size)
input_shape = (1,) + ds_info.features["image"].shape
num_classes = ds_info.features["label"].num_classes
iter_per_epoch_train = ds_info.splits['train'].num_examples // FLAGS.train_batch_size
iter_per_epoch_test = ds_info.splits['test'].num_examples // FLAGS.test_batch_size
net = CNN(num_classes)
@jax.jit
def accuracy(params, data):
inputs, labels = data
logits = net.apply({"params": params}, inputs)
return jnp.mean(jnp.argmax(logits, axis=-1) == labels)
logistic_loss = jax.vmap(loss.multiclass_logistic_loss)
@jax.jit
def loss_fun(params, l2reg, data):
"""Compute the loss of the network."""
inputs, labels = data
x = inputs.astype(jnp.float32)
logits = net.apply({"params": params}, x)
sqnorm = tree_util.tree_l2_norm(params, squared=True)
loss_value = jnp.mean(logistic_loss(labels, logits))
return loss_value + 0.5 * l2reg * sqnorm
@jax.jit
def pgd_attack(image, label, params, epsilon=0.1, maxiter=10):
"""PGD attack on the L-infinity ball with radius epsilon.
Args:
image: array-like, input data for the CNN
label: integer, class label corresponding to image
params: tree, parameters of the model to attack
epsilon: float, radius of the L-infinity ball.
maxiter: int, number of iterations of this algorithm.
Returns:
perturbed_image: Adversarial image on the boundary of the L-infinity ball
of radius epsilon and centered at image.
Notes:
PGD attack is described in (Madry et al. 2017),
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.06083.pdf
"""
image_perturbation = jnp.zeros_like(image)
def adversarial_loss(perturbation):
return loss_fun(params, 0, (image + perturbation, label))
grad_adversarial = jax.grad(adversarial_loss)
for _ in range(maxiter):
# compute gradient of the loss wrt to the image
sign_grad = jnp.sign(grad_adversarial(image_perturbation))
# heuristic step-size 2 eps / maxiter
image_perturbation += (2 * epsilon / maxiter) * sign_grad
# projection step onto the L-infinity ball centered at image
image_perturbation = jnp.clip(image_perturbation, - epsilon, epsilon)
# clip the image to ensure pixels are between 0 and 1
return jnp.clip(image + image_perturbation, 0, 1)
# Initialize solver and parameters.
solver = OptaxSolver(
opt=optax.adam(FLAGS.learning_rate),
fun=loss_fun,
maxiter=FLAGS.epochs * iter_per_epoch_train)
key = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
params = net.init(key, jnp.zeros(input_shape))["params"]
state = solver.init_state(params)
start = datetime.datetime.now().replace(microsecond=0)
jitted_update = jax.jit(solver.update)
accuracy_train = []
accuracy_test = []
adversarial_accuracy_train = []
adversarial_accuracy_test = []
for it in range(solver.maxiter):
# training loop
images, labels = next(train_ds)
# convert images to float as attack requires to take gradients wrt to them
images = images.astype(jnp.float32) / 255
adversarial_images_train = pgd_attack(
images, labels, params, epsilon=FLAGS.epsilon)
# train on adversarial images
params, state = jitted_update(
params=params,
state=state,
l2reg=FLAGS.l2reg,
data=(adversarial_images_train, labels))
# Once per epoch evaluate the model on the train and test sets.
if state.iter_num % iter_per_epoch_train == iter_per_epoch_train - 1:
# compute train set accuracy, both on clean and adversarial images
adversarial_accuracy_train_sample = 0.
accuracy_train_sample = 0.
for _ in range(iter_per_epoch_train):
images, labels = next(train_ds)
images = images.astype(jnp.float32) / 255
accuracy_train_sample += jnp.mean(accuracy(params, (images, labels))) / iter_per_epoch_train
adversarial_images_train = pgd_attack(
images, labels, params, epsilon=FLAGS.epsilon)
adversarial_accuracy_train_sample += jnp.mean(
accuracy(params, (adversarial_images_train, labels))) / iter_per_epoch_train
accuracy_train.append(accuracy_train_sample)
adversarial_accuracy_train.append(adversarial_accuracy_train_sample)
# compute train set accuracy, both on clean and adversarial images
adversarial_accuracy_test_sample = 0.
accuracy_test_sample = 0.
for _ in range(iter_per_epoch_test):
images, labels = next(test_ds)
images = images.astype(jnp.float32) / 255
accuracy_test_sample += jnp.mean(accuracy(params, (images, labels))) / iter_per_epoch_test
adversarial_images_test = pgd_attack(
images, labels, params, epsilon=FLAGS.epsilon)
adversarial_accuracy_test_sample += jnp.mean(
accuracy(params, (adversarial_images_test, labels))) / iter_per_epoch_test
accuracy_test.append(accuracy_test_sample)
adversarial_accuracy_test.append(adversarial_accuracy_test_sample)
time_elapsed = (datetime.datetime.now().replace(microsecond=0) - start)
print(f"Epoch {it // iter_per_epoch_train} out of {FLAGS.epochs}")
print(f"Accuracy on train set: {accuracy_train[-1]:.3f}")
print(f"Accuracy on test set: {accuracy_test[-1]:.3f}")
print(
f"Adversarial accuracy on train set: {adversarial_accuracy_train[-1]:.3f}"
)
print(
f"Adversarial accuracy on test set: {adversarial_accuracy_test[-1]:.3f}"
)
print(f"Time elapsed: {time_elapsed}")
print()
/opt/conda/envs/jaxopt/lib/python3.10/site-packages/jax/_src/tree_util.py:188: FutureWarning: jax.tree_util.tree_multimap() is deprecated. Please use jax.tree_util.tree_map() instead as a drop-in replacement.
warnings.warn('jax.tree_util.tree_multimap() is deprecated. Please use jax.tree_util.tree_map() '
Epoch 0 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.982
Accuracy on test set: 0.982
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.979
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.979
Time elapsed: 0:00:14
Epoch 1 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.987
Accuracy on test set: 0.986
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.984
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.982
Time elapsed: 0:00:21
Epoch 2 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.989
Accuracy on test set: 0.987
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.986
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.984
Time elapsed: 0:00:29
Epoch 3 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.992
Accuracy on test set: 0.990
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.990
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.988
Time elapsed: 0:00:36
Epoch 4 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.994
Accuracy on test set: 0.990
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.992
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.988
Time elapsed: 0:00:43
Epoch 5 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.994
Accuracy on test set: 0.990
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.992
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.987
Time elapsed: 0:00:51
Epoch 6 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.995
Accuracy on test set: 0.991
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.994
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.988
Time elapsed: 0:00:58
Epoch 7 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.995
Accuracy on test set: 0.990
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.993
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.988
Time elapsed: 0:01:05
Epoch 8 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.995
Accuracy on test set: 0.989
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.993
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.987
Time elapsed: 0:01:13
Epoch 9 out of 10
Accuracy on train set: 0.995
Accuracy on test set: 0.990
Adversarial accuracy on train set: 0.993
Adversarial accuracy on test set: 0.988
Time elapsed: 0:01:20
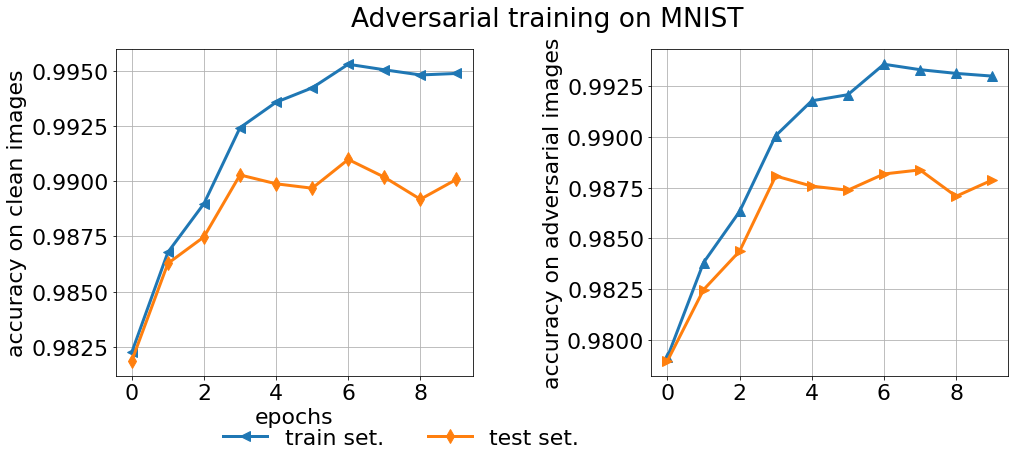
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(16, 6))
plt.suptitle("Adversarial training on " + f"{FLAGS.dataset}".upper())
axes[0].plot(accuracy_train, lw=3, label="train set." , marker='<', markersize=10)
axes[0].plot(accuracy_test, lw=3, label="test set.", marker='d', markersize=10)
axes[0].grid()
axes[0].set_ylabel('accuracy on clean images')
axes[1].plot(
adversarial_accuracy_train,
lw=3,
label="adversarial accuracy on train set.", marker='^', markersize=10)
axes[1].plot(
adversarial_accuracy_test,
lw=3,
label="adversarial accuracy on test set.", marker='>', markersize=10)
axes[1].grid()
axes[0].legend(frameon=False, ncol=2, loc='upper center', bbox_to_anchor=(0.8, -0.1))
axes[0].set_xlabel('epochs')
axes[1].set_ylabel('accuracy on adversarial images')
plt.subplots_adjust( wspace=0.5 )
plt.show()
Find a test set image that is correctly classified but not its adversarial perturbation
def find_adversarial_imgs():
for _ in range(iter_per_epoch_test):
images, labels = next(test_ds)
images = images.astype(jnp.float32) / 255
logits = net.apply({"params": params}, images)
labels_clean = jnp.argmax(logits, axis=-1)
adversarial_images = pgd_attack(
images, labels, params, epsilon=FLAGS.epsilon)
labels_adversarial = jnp.argmax(net.apply({"params": params}, adversarial_images), axis=-1)
idx_misclassified = jnp.where(labels_clean != labels_adversarial)[0]
if len(idx_misclassified) == 0:
continue
else:
for i in idx_misclassified:
img_clean = images[i]
prediction_clean = labels_clean[i]
if prediction_clean != labels[i]:
# the clean image predicts the wrong label, skip
continue
img_adversarial = adversarial_images[i]
prediction_adversarial = labels_adversarial[i]
# we found our image
return img_clean, prediction_clean, img_adversarial, prediction_adversarial
raise ValueError("No mismatch between clean and adversarial prediction found")
img_clean, prediction_clean, img_adversarial, prediction_adversarial = \
find_adversarial_imgs()
_, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(6*3, 6))
axes[0].set_title('Clean image \n Prediction %s' % int(prediction_clean))
axes[0].imshow(img_clean, cmap=plt.cm.get_cmap('Greys'), vmax=1, vmin=0)
axes[1].set_title('Adversarial image \n Prediction %s' % prediction_adversarial)
axes[1].imshow(img_adversarial, cmap=plt.cm.get_cmap('Greys'), vmax=1, vmin=0)
axes[2].set_title(r'|Adversarial - clean| $\times$ %.0f' % (1/FLAGS.epsilon))
axes[2].imshow(jnp.abs(img_clean - img_adversarial) / FLAGS.epsilon, cmap=plt.cm.get_cmap('Greys'), vmax=1, vmin=0)
for i in range(3):
axes[i].set_xticks(())
axes[i].set_yticks(())
plt.show()
